-
Antibiofilm ability of harmaline and norharmane from Peganum harmalaAntimicrobial Agent 2022. 2. 19. 18:58반응형
As the day goes, the problem with antibiotic-resistant bacteria is getting serious and usually, they are apt to form biofilms which mean they are serious pathogens. So many people have been trying to find an efficient way to deal with them. There are many other ways to deal with antibiotic-resistant bacteria and one interesting way to fight against them is by inhibiting their biofilm formation. Antibiofilm activities of norharmane and its derivatives against Escherichia coli O157:H7 and other bacteria is a paper about the antibiofilm ability of Peganum harmala extract.
Peganum harmala is a plant usually found in the Middle East and South Asia. It has been reported to have vasorelaxant, antileishmanial, antiplasmodial, and antimicrobial activities. The researchers extracted alkaloids from P. harmala and tested them on Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacteria. By the way, these two that I’ve just mentioned cause a large number of foodborne problems and I guess that’s why the authors tested on them. Especially E. coli O157:H7 causes hemolytic-uremic syndrome development which is fatal to human beings. Plus, it colonizes and forms a biofilm at the large intestine and causes bloody diarrhea as they make lesions. P. aeruginosa is a bacterium that causes an opportunistic infection which means it’s living with us. However, due to the usage of a large number of antibiotics, they developed tolerance against antibiotics. So if there’s a wound, it can invade our body and cause serious sepsis that couldn’t be treated with antibiotics. Also, they form biofilms on surfaces like cystic fibrosis-affected tissues in the lungs(biotic surfaces) and on abiotic surfaces like contact lenses, catheter lines (a tube to drain out urine from the bladder), and contaminated surgical equipment which means it is apt to cause nosocomial infection. Therefore, it’s important to study these 2 bacteria and I guess this is one of the reasons that the authors studied mainly about antibiofilm effect of P. aeruginosa against these 2 bacteria (they also operated experiments against other bacteria including MRSA, MSSA, Paenibacillus alvei, Staphylococcus epidermis, Shewanella oneidensis, Providencia stuartti. Plus they have tested several different strains of these)
Plants contain plentiful alkaloids and these compounds are known to have various pharmacological effects. According to this study, they have separated 13 different alkaloids from different species. They tested antibiofilm abilities of harmaline against 10 other bacterial strains. Norharmane and its derivatives are present in the seeds of P. aeruginosa L.(Nitrariaceae). There are normine, 6-methoxyharmalan, harmol, and harmane. After their test, they used a confocal microscope, electron microscope, and motility analytic to check biofilm reduction, action. Finally, as an in vivo model, Caenorhabditis elegans killing assay was conducted to figure out the effect of harmaline(50μg/ml), norharmane(20μg/ml), and DMSO(0.1% v/v) on E. coli O157:H7 virulence.

Alkaloids they have extracted for the project. They inoculated bacteria and introduced the alkaloids into the inoculated medium. After that, they stained biofilms with crystal violet. Also, cinnamaldehyde was used as the positive control as there’s a study about antibiofilm inhibition against E. coli O157H:7 or P. aeruginosa PAO1. As harmaline and norharmane was the strongest biofilm inhibitor, they focused on these 2 compounds.
In the case of harmaline, it was very effective to E. coli O157:H7 and dose-dependently affecting the growth of it, and moderately effective to other bacteria. At the concentration of 100μg/ml, harmaline decreased the biofilm formation of E. coli O157H7. However, against other bacteria, the inhibition of their biofilm formation was not dose-dependent, which means it could inhibit their biofilm formation, but not as effective as it does to E. coli O157:H7.

As harmaline is a derivative of norharmane, they have conducted the same thing with its other derivatives. As a result, at the concentration of 50μg/ml, norharmane, harmine, 6-methoxyharmalan, and harmane inhibited E. coli O157:H7 biofilm formation by over 50% versus the untreated control. Something interesting was that norharmane was more effective than harmaline that’s because of their structural difference. The absence of a methyl group at C-1 was important for antibiofilm activity. Also compared with harmol, harmaline has methoxyl group at C-7 rather than hydroxyl group. Plus, norharmane dose-dependently inhibited biofilm formation of P. aeruginosa PAO1 and PA14. With this information, we can find out that structural features play a huge role.

These results indicate that harmaline and norharmane have the strongest ability to reduce biofilm formation. Compared with cinnamaldehyde at the concentration of 100μg/ml, the ability to inhibit biofilm formation of harmaline, norharmane, harmine, harmane was stronger than that of it.
They have begun swimming and swarming motility assay as these abilities are directly related to biofilm formation. To better form biofilm, they should be arranged in the proper place. Therefore, they used harmaline(50μg/ml) and norharmane(20μg/ml) to see whether they can inhibit their motility. The result was successful. In the case of comparing swarming inhibition, cinnamaldehyde was stronger than both harmaline and norharmane but in the case of swimming inhibition, norharmane was stronger than harmaline and cinnamaldehyde. The strengths of them were different, but anyway, through this experiment, they proved that harmaline and norharmane can reduce the biofilm formation of E. coli O157:H7.

For their last experiment, they conducted in vivo test on a nematode; C. elegans. Many bacteria like E. coli O157:H7 can form biofilms in the digestive tract of C. elegans and this can lead to its death. Harmaline(50μg/ml) and norharmane(20μg/ml) prolonged the lifespan of E. coli O157:H7 infected C. elegans.
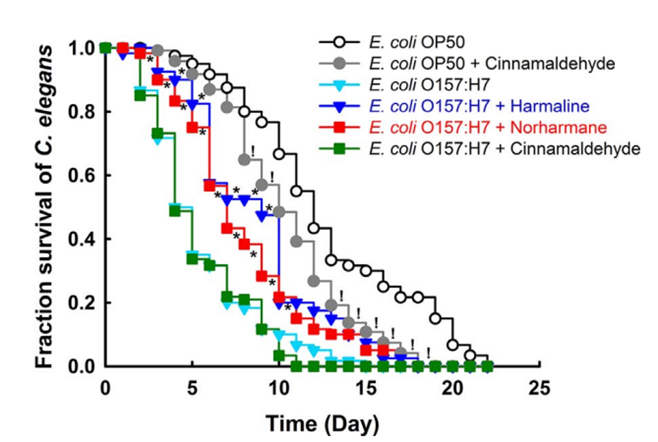
Harmaline and norharmane showed some toxicity in the model of nematode at above 100μg/ml, but harmaline at 20μg/ml showed no toxicity. However, as we can see at the graph, cinnamaldehyde didn’t make a meaningful result.
Through these experiments, the researchers concluded that harmaline and norharmane from the extracts can inhibit biofilm formation against E. coli O157:H7 and P. aeruginosa strains. Especially against E. coli O157:H7, they inhibited fimbriae formation, reduced their motility which directly leads to a decrease of biofilm formation. Also, the most important point of this study is β-carboline backbone and functional groups at the C-1 and C-7 positions are important for their antibiofilm effect on E. coli O157:H7. Plus, norharmane and harmaline had indole moiety which is a famous biofilm modulator against various bacteria like E. coli O157:H7 and P. aeruginosa. At the end, they found that with the proper concentration of harmaline and norharmane, they can elongate the life span of E. coli O157:H7 infected C. elegans which means that there is a possibility that they could be used to human beings.
반응형'Antimicrobial Agent' 카테고리의 다른 글